State educational institution of higher professional education
ST. PETERSBURG STATE UNIVERSITY
TELECOMMUNICATIONS NAMED AFTER. PROF. M.A. BONCH BRUEVICH
Arkhangelsk College of Telecommunications (branch) of St. Petersburg State University of Telecommunications named after prof. M.A. Bonch-Bruevich
COURSE PROJECT
on the topic: “Computer network project for the commercial enterprise“ NordSoft ””
K309 10KP01. 006 PZ
The discipline "Computer networks and telecommunications"
Student: S.O. Maksimov
Teacher: V.S. Kulebyakina
Arkhangelsk - 2010
Content Introduction 1. Brief description of the company 2. Topology Selection 3. Organization of a local area network in offices 3.1 Networking in a head office 3.2 Networking in a second office 3.2.1 Basic Ethernet concepts 3.2.2 Connectivity devices4. Network Technology Selection5. Calculation of access time to the station to the network
6. Equipment summary table
Conclusion List of sources used
Introduction
The entry of Russia into the global information space entails the widest use of the latest information technologies, and first of all, computer networks. At the same time, the user's abilities sharply increase and qualitatively change both in providing services to their customers and in solving their own organizational and economic problems.
Today, there are many computer databases and data banks on various aspects of human activity. To access the information stored in them, you need a computer network. Networks break into people's lives, both in professional activities and in everyday life - in the most unexpected and massive way, knowledge about networks and skills in them become necessary for many people. Computer networks spawned new information processing technologies - network technologies. In the simplest case, network technologies allow the sharing of resources - mass storage devices, printing devices, Internet access, databases and data banks. The most modern and promising approaches to networks are associated with the use of the collective division of labor when working together with information - the development of various documents and projects, managing an institution or enterprise, etc.
To organize a local area network (LAN), Ethernet technology is used, which appeared back in the 70s of the last century. Ethernet technology distinguishes several types of building a distributed computing system based on its topological structure. A local network topology is a configuration of cable connections between computers made according to a single principle. The specific topology is selected based on the equipment used, as well as on the basis of the existing requirements for mobility, scalability and computing power of the entire system as a whole.
This course project considers the organization of a LAN in two offices of the company "NordSoft", the choice of topology and determines the necessary hardware and software. In addition, the choice of technology and telecom operator for organizing a single network, i.e. communication of offices among themselves.
1. Brief description of the company
The company "NordSoft" - a small business. The main activity of the company is the sale of computer equipment, software, network equipment and peripherals of world famous companies. The company offers high-tech products and software.
The company employs 20 people. The organizational structure includes two departments:
1) The main office is the sales department, which is engaged in the sale, purchase of products, search and work with customers, advertising and marketing, and also records and analyzes financial and economic activities, planning, forecasting.
2) The secondary office is engaged in transportation, assembly, packaging of goods. The secondary office has a storage room.
Figure 1 - Territorial layout of offices
The wholesale market for personal computers in which NordSoft operates is characterized by fierce competition. The prices for the same goods from different companies are approximately the same, and those that have any competitive advantages and differences win in the competition. For example, convenient location of the office, speed of service, maintaining the right assortment, discounts for regular customers, the ability to deliver goods, free advertising materials for decoration of outlets, polite staff, an individual approach to especially valuable customers, loans, etc.
The NordSoft company occupies a profitable market niche: it has well-established commercial relations with a large buyer, provided with stable state financing. Thus, the main advantage of the organization under study is stability, the establishment of business contacts, guarantees for ensuring activities and obtaining minimal profits in the absence of the need for a constant search for new sales markets.
The company "NordSoft" conducts its main activities in two geographically distributed offices, in each of which should be organized one of the parts of a single LAN. Both offices are geographically distributed within the city (Figure 1), therefore, to organize a single network, it is necessary to connect LAN elements through communication networks existing in the city.
One of the offices is located in the city center in the business center, which already has a structured cabling system (SCS). SCS allows you to use the existing cable infrastructure to create one of the parts of the LAN. The main office of the enterprise is located in two offices, in which there are two laptops. Each laptop has a Wi-Fi adapter, a network operating system Windows 7 Enterprise, which was specifically designed for business. An accountant who uses the 1C: Accounting program will work on one of the laptops. Also in this office is the director of the company, secretary and customer service manager. All employees will need a scanner, printer, fax for convenient layout of documents.
The second office of the company is located in another part of the city. This office organizes the main production activities. The room has a large area and several workplaces are organized on the territory. A server with the installed Windows Server 2003 operating system will be installed in this room, where general company documents will be saved.
2. The choice of topology
The purpose of this section is to fully substantiate the choice of a specific LAN topology for each of the company's offices.
In general, the term “topology,” or “network topology,” describes the physical location of computers, cables, and other network components. The network topology determines its characteristics. In particular, the choice of a particular topology affects:
The composition of the necessary network equipment;
On the characteristics of network equipment;
On the possibility of expanding the network;
On the way to manage the network.
Each network topology imposes a number of conditions. For example, it can dictate not only the type of cable, but also the way it is laid. A topology can also determine how computers interact on a network. Different types of topologies correspond to different interaction methods, and these methods have a big impact on the network.
All networks are built on the basis of three basic topologies: bus (bus), star (star), ring (ring). If computers are connected along one cable (segment), the topology is called the “Bus”. When computers are connected to cable segments originating from a single point or hub, the topology is called the Star. If the cable to which the computers are connected is closed in a ring, this topology is called the “Ring”.
As mentioned above, the main office of the enterprise is located in two offices, in which there are two laptops (Figure 2).
On laptops there is a built-in Wi-Fi adapter, the network operating system is Windows 7 Enterprise. The Wi-Fi adapters of these computers must support all current IEEE 802.x standards.

Figure 2 - Location of LAN workstations in the main office
Wi-Fi technology allows you to deploy a network without laying a cable, which can reduce the cost of deployment, which is important for small businesses, or expand the network. Wi-Fi technology is very convenient since you are not tied to a wired computer network. You can work at your desk or move to other rooms, while remaining in the network coverage area. In the second office we install a scanner, printer, fax, which will be connected to laptops. We give the characteristics of the laptops used in table 1.
Table 1 - Notebook Specifications
All laptops will be connected to one central device - a router (router). A router is a network device that makes decisions about forwarding network layer packets between different network segments. The router will be connected to the structured cabling system of the business center building.
In the second office, where the main production activities are organized, it is better to take the Star topology as the basis.
There are no such serious problems in this topology when a cable is broken or a workstation fails. If only one computer fails (or the cable connecting it to the hub), then only this computer will not be able to transmit or receive data over the network. It will not affect other computers on the network. Otherwise, if the cable was disconnected or broken, all employees of the company would not be able to exchange documents for some time, which would lead to loss of profit.
Since computers are located in different parts of the office building (Figure 3) and the warehouse building, centralized control and management of workstations will be more effective than setting up a separate machine for working on the network. In the office of the main production, there are ten computers intended for the main work of specialists and one computer of the network administrator. This is the host computer or server.

Figure 3 - Location of LAN workstations in the second office
The server allows you to manage all the computers in this office, monitor their performance, provide security and Internet access. He receives network settings from the provider, then distributes the parameters in a certain algorithm to other computers. Computers on the network must have a standard network card with an RJ45 connector and a network operating system. We give the characteristics of the computers used in the second office in table 2.
Table 2 - Characteristics of workstations and servers
In the "Star" topology, you do not need to bother with the purchase and installation of additional network cards, since only one network cable is laid to the hub. Adding new computers, which is quite possible when expanding a business, is easy to modify this network.
A star topology is the fastest of all computer network topologies. The frequency of information transfer requests is relatively low when compared with other topologies.
All computers are connected to a central point; for large networks, cable consumption is significantly increased. In addition, if the central component fails, the operation of the entire network is disrupted. So you need to focus on the choice of network equipment. So, the selected topology is presented in Figure 4.
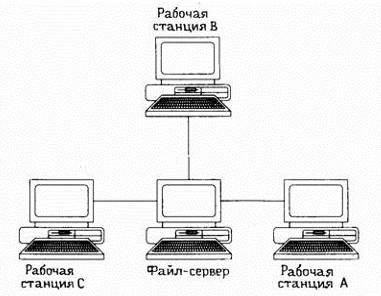
Figure 4 - Network topology in the main and main offices
3. Organization of a local area network in offices
3.1 Networking at the head office
Network technologies, and in particular, wireless networks, are becoming deeper and stronger every day in our daily lives. Nowadays, it is simply impossible to imagine a modern office without computers, the Internet, a local network and reliable protection. Network technologies based on a wireless (Wi-Fi) connection will allow you to be connected to the network without the need to constantly connect a wire to your computer - you can exchange data, communicate, while remaining free in space.
Increasingly evolving technologies, an expanding range of compatible equipment, constantly improving standards and more reliable protection - all this makes Wi-Fi a tempting offer for use in large and small corporate networks. The latest developments and the latest equipment will satisfy the most modern requirements for speed, reliability and security of the connection. Since employees will use laptops with built-in Wi-Fi adapters at the main office, they are better off using a wireless network. The block diagram is shown in Figure 5.
In our case, the router will be connected to the horizontal subsystem of the SCS building, where there is Internet access. SCS describes the European standard EN 50173-1. Communication between offices will be through VPN technology.
The main equipment for a Wi-Fi network is an access point, a router and a Wi-Fi adapter.
Access Point (Access Point) - this device in a wireless network performs functions similar to a switch (or hub) in conventional wired structures.

Figure 5 - Block diagram of a Wi-Fi network
The access point integrates several Wi-Fi devices into one network and must be connected to a router (router) or server to access the Internet. In addition, the access point can provide a connection to the print server and combine wired and wireless networks.
A router (Router, Gateway) is essentially the same access point, but with additional features. Using a router, you can connect directly to the Internet using an Ethernet cable or telephone line with an ADSL (STREAM) connection connected. In our case, an Ethernet cable of the SCS building will be connected to it, where there is Internet access. In addition, the router has built-in software that allows you to configure security policies and access filtering.
An adapter is a device that installs directly into a computer so that it "sees" the wireless network. Adapters come in several varieties - PCI (internal to a desktop computer), USB (external to a desktop or laptop), PCMCIA (internal to a laptop) or built-in. Our employees, of course, will use the built-in adapters.
Typically, a Wi-Fi network diagram contains at least one access point and at least one client. It is also possible to connect two clients in point-to-point mode when the access point is not used, and the clients are connected via network adapters "directly". The access point transmits its network identifier (SSID) using special signal packets at a speed of 0.1 Mbps every 100 ms. So 0.1 Mbps is the lowest bit rate for Wi-Fi. Knowing the SSID of the network, the client can find out whether it is possible to connect to this access point. If two access points with identical SSIDs fall into the coverage area, the receiver can choose between them based on signal strength data. The Wi-Fi standard gives the client complete freedom in choosing the criteria for the connection.
When choosing a standard for network equipment, it is necessary to take into account the degree of security, data transfer rate and price for this device. The components and characteristics of wireless networks are defined by the IEEE 802.11 family of standards. This standard is part of the IEEE 802.x series, which also includes the standards 802.3 Ethernet, 802.5 Token Ring, etc. Today, there are several different standards for wireless connections. The main ones are 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g and 802.11i. These standards differ both in the maximum possible data transfer rate and in range. In accordance with these standards, the type of equipment is selected. In Russia at the moment, in the vast majority, only two of them are used - these are 802.11b and 802.11g. In addition, a new 802.11n standard is being developed, which may soon become the main one.
The IEEE 802.11g standard is the most affordable and popular standard that network routers use. IEEE 802.11g standard - operates at a frequency of 2.4 GHz, supports a connection speed of up to 54 Mbps. It is the most advanced of the common formats. It replaced 802.11b and supports five times faster data transfer rates and a much more advanced security system. Devices of this standard are backward compatible with 802.11b devices. This means that mixed networks consisting of 802.11b and 802.11g devices can work. Now the cost of 802.11g devices is almost equal to the cost of similar in functionality 802.11b devices, while providing a five-fold increase in speed. Therefore, it hardly makes sense to build new networks on 802.11b equipment. The security level of wireless networks on this standard has also significantly increased. With proper tuning, it can be rated as high. This standard supports the use of WPA and WPA2 encryption protocols, which provide a much higher level of protection than the WEP protocol used in the 802.11b standard. The network range is 50 m. An example of an IEEE 802.11g standard router is shown in Figure 6.

Figure 6 - IEEE 802.11g and IEEE 802.11b Router
You need to pay attention to the fact that in wireless networks, the connection speed and the transfer rate of useful data are significantly different. At a connection speed of 54 Mbit / s, the actual data transfer rate is usually 22–26 Mbit / s.
Despite the most modern technologies, one should always remember that high-quality data transfer and a reliable level of security are ensured only by the correct configuration of equipment and software.
3.2 Networking in the second office
3.2.1 Ethernet Concepts
The second office has a large room, and in order to integrate computers into a network, the Zvezda topology with Ethernet data transfer technology will be used.
Ethernet is a packet data transmission technology mainly of local computer networks. Ethernet technology is the most common LAN technology. Ethernet technology is the most common LAN technology.
Ethernet standards define wired connections and electrical signals at the physical layer, frame format and media access control protocols - at the data link layer of the OSI model. Ethernet is mainly described by IEEE 802.3 standards. Ethernet became the most common LAN technology in the mid-90s of the last century, displacing legacy technologies such as Arcnet, FDDI, and Token ring.
Access control method (for a network on a coaxial cable) - multiple access with carrier control and collision detection (CSMA / CD, Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection), data transfer rate 10 Mbps, packet size from 72 to 1526 bytes, described data encoding methods. The operating mode is half duplex, that is, the node cannot simultaneously transmit and receive information. The number of nodes in one shared network segment is limited by the limit of 1024 workstations (physical layer specifications can set more stringent restrictions, for example, no more than 30 workstations can be connected to a thin coaxial segment, and no more than 100 to a thick coaxial segment). However, a network built on one shared segment becomes inefficient long before the limit of the number of nodes is reached, mainly due to half-duplex operation.
In Ethernet technology, the data link layer (data link layer) has two sublevels: Logical Link Control (LLC) and Media Access Control (MAC). The LLC layer is responsible for the flow and control of errors at the data link layer (link layer). The MAC sublayer is responsible for the operation of the CSMA / CD access method. This sublayer also creates data received from the LLC layer and transmits frames to the physical layer for encoding. The physical layer converts the data into electrical signals and sends them to the next station through the transmission medium. This core layer also detects conflicts and reports them to the data link layer (link layer).
An Ethernet network has one type of frame containing seven fields: the preamble, the start of the frame is SFD, the endpoint address is DA, the source address is SA, the length / type of protocol unit is the PDU and the cyclic redundancy code.
The local Ethernet network does not provide a mechanism to confirm receipt of frames. Confirmation is implemented at higher levels. The CSMA / CD MAC frame format is shown in Figure 7.

Figure 7 - CSMA / CD MAC frame format
The frame preamble contains 7 bytes (56 bits) of alternating zeros and ones, which alert the system to receive an incoming frame and prepare it for synchronization using clock pulses. The preamble is actually added at the physical level and is not (formally) part of the frame.
Start Frame Delimiter (SFD). The SFD field (1 byte: 10101011) marks the beginning of the frame and indicates to the station the end of synchronization. The last two bits - 11 - signal that the next field is the address of the recipient.
The DA (Destination Address) field is 6 bytes long and contains the physical address of the destination station or intermediate link.
Field SA (Source Address) also has 6 bytes and contains the physical address of the transmitting or intermediate station.
The type / length field has one of two values. If the field value is less than 1518, this is the length field and determines the length of the data field that follows. If the value of this field is greater than 1536, it defines the upper level protocol that is used to serve the Internet.
The data field carries data encapsulated from the upper layer protocols. This is a minimum of 46 and a maximum of 1,500 bytes.
Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC). The last field in these frames according to the 802.3 standard contains information for error detection, in this case CRC - 32.
When designing the Ethernet standard, it was stipulated that each network card (as well as the built-in network interface) should have a unique six-byte number (MAC address), which was flashed into it during manufacture. This number is used to identify the sender and receiver of the frame, and it is assumed that when a new computer (or other device capable of working on the network) appears on the network, the network administrator does not have to configure the MAC address.
The uniqueness of MAC addresses is achieved by the fact that each manufacturer receives a range of sixteen million (2 ^ 24) addresses from the IEEE Registration Authority Steering Committee, and, as the allocated addresses are exhausted, they can request a new range. Therefore, the three high-order bytes of the MAC address can determine the manufacturer. It is usually written in the hexadecimal notation to separate bytes, for example: 07-01-02-01-2C-4B.
The need for higher data rates has created the Fast Ethernet Fast Ethernet protocol (100 Mbps). At the MAC layer, Fast Ethernet uses the same principles as traditional Ethernet (CSMA / CD), except that the transmission speed has been increased from 10 Mbps to 100 Mbps. For CSMA / CD to work, there are two options: either increase the minimum frame length or decrease the collision domain
Increasing the minimum frame length requires an additional header. If the data to be sent is not long enough, we will need to add additional bytes, which entails an increase in the transmitted overhead information and a loss of efficiency.
Fast Ethernet chose a different path: the collision domain was reduced by a factor of 10 (from 2500 meters to 250 meters). This stellar topology of 250 meters is acceptable in many cases. At the physical layer, Fast Ethernet uses various signal transmission methods and various media in order to achieve a data transfer rate of 100 Mbps.
It is better to use Fast Ethernet technology in our project, since a speed of 100 Mbps is quite satisfactory for us, and all modern hubs support this technology
Comparing all categories of Twisted Pair cable, it is better to use Category 5 twisted pair cable as a physical medium for data transfer (Figure 8). It satisfies our condition in data transfer rate and is the most common type of cable and has a low price. Also, twisted pair cable works in duplex mode, has higher network reliability in case of cable faults and greater noise immunity when using a differential signal.
CAT5 (frequency 100 MHz) is a four-pair cable used in the construction of 100BASE-TX and for the construction of telephone lines, supports a data transfer rate of up to 100 Mbit / s when using 2 pairs. He came to replace the third category.

Figure 8 - Twisted-pair Category 5
Since all computers are connected to a central point, cable consumption increases significantly. Based on the size of the second office (20x12), we will purchase 200 meters of cable and 10 connectors. It is better to crimp the cable according to the EIA / TIA-568B standard, since it is used more often. When installing a twisted-pair cable, the maximum permissible bending radius (8 external cable diameters) must be maintained - strong bending can lead to an increase in external interference to the signal or lead to destruction of the cable sheath.
When installing shielded twisted pairs, it is necessary to monitor the integrity of the screen along the entire length of the cable. Stretching or bending leads to destruction of the screen, which leads to a decrease in resistance to pickups.
3.2.2 Connection devices
Today, a conventional network consists of many local networks and one or more core networks. Therefore, technologies must provide ways to integrate these networks. Tools designed for this purpose are called connection devices.
Our network consists of a small number of machines, only one hub will be used, to which a server and a global Internet cable will be connected, so that through VPN technology it can communicate with the main office. The server will dynamically assign IP addresses to computers on the network through the DHCP service. As the server operating system will be used Windows Server 2003.
Repeaters and hubs operate at the first level of the TCP / IP protocol suite (This is comparable to the physical layer of the OSI model.).
Repeaters are used to increase the length of a common network consisting of different cable segments. The repeater is a level 1 device and works only at the physical level. Signals that carry information within a network can travel a fixed distance up to the point where attenuation threatens data integrity. The repeater receives the signal, and before it becomes too weak or distorted, it restores the original bit pattern. Then it transmits the regenerated signal.
It receives signals from one cable segment and repeats them bit by bit on the other cable segment, increasing power and improving the shape of the pulses. The use of a repeater introduces an additional delay and worsens the recognition of collisions, therefore, their number in the Ethernet network should not exceed 4, while the maximum length of one segment should be no more than 500 meters, and the diameter of the entire network should not exceed 2500 meters.
Note that the network formed by the relays is still considered a single local network, but the part of the network separated by the relays is called a segment. The repeater acts as a node with two interfaces, but works only at the physical level. When it receives a packet from any of the interfaces, it restores and passes it forward to another interface. The relay transmits each packet forward, but does not have any capabilities for extracting and redirecting information.
The nodes are connected to each other through a central device - a hub. Although in the general sense the term “hub” can be applied to any connection device, in this case it has a special meaning.
A hub is actually a multi-input repeater. It is commonly used to create a connection between stations in a physical stellar topology. The hub (Hub) is a level 1 device and performs the functions of a repeater on all segments of twisted pairs between the hub and the node, except for the port from which the signal is received. Each port has a receiver (R) and a transmitter (T). In addition, the hub itself detects a collision and sends a jam sequence to all its outputs. Typical hub capacity is from 8 to 72 ports. Hubs can also be used to propagate hierarchy levels, as shown in Figure 9.

Figure 9 - Hubs
Hubs can be connected to each other using the same ports that are used to connect the nodes. The standard allows connecting hubs only in tree structures, any loops between the ports of the hub are prohibited. For reliable recognition of a collision between any two nodes, there should be no more than 4 hubs, while the maximum length between the hubs should be no more than 100 meters, and the diameter of the entire network should be no more than 500 meters.
4. The choice of network technology
To connect existing networks, virtual private network (VPN) technology will be used. Networks can implement the transfer of information over secure communication channels, which guarantees the implementation of information security and the safety of the entire network. Dedicated communication channels can also ensure the implementation of these requirements, but the stability of the dedicated channel will be very high. The structure of a virtual private network is shown in Figure 10.
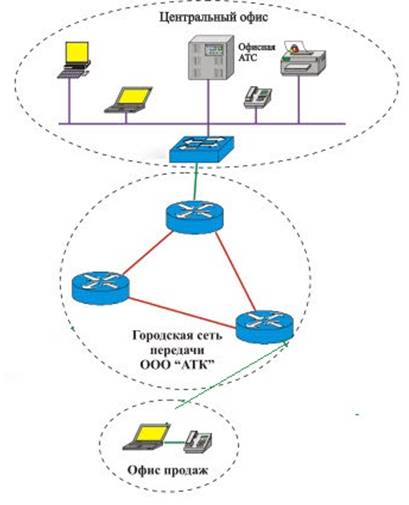
Figure 10 - Virtual Private Network Between Offices
VPN technology provides guaranteed bandwidth, security, as well as almost complete secrecy of the transmitted information. VPN technology allows for the integration of remote local networks using hardware and software. The technology itself allows the implementation of information protection of transit traffic. In VPN technology, information is transmitted in the form of packets; they are tunneled over public networks. VPN technology uses end-to-end security solutions. Cryptographic methods of protection are used here and, in addition, continuous monitoring is carried out over the implementation of all information security methods. VPN technology also guarantees quality of service for user data.
It is customary to distinguish three main types: VPN with remote access (Remote Access VPN), corporate VPN (Intranet VPN) and corporate VPN (ExtranetVPN). In our case, the Intranet will be used, since the network will be used only within the company (cooperative). Intranet VPNs are also called point-to-point, or LAN-LAN VPNs. It extends secure private networks to the entire Internet or other public networks. The intranet allows the use of IP tunneling methods such as: GRI, L2TP, IPSec. To ensure high reliability in information protection, the operator providing VPN services uses information encryption in the channel itself, in addition, the operator must provide a certain level of quality of service (QoS) in the channel. It should be borne in mind that QoS depends on the application level.
In practical implementation, there are several options for the location of VPN devices relative to other devices. If the firewall is located before the VPN gateway relative to the user's network, then all traffic is transmitted through the gateway. The disadvantage of such schemes is the openness of the gateway for all attacks from the public network. If the firewall is located after the VPN gateway relative to the user's network, then the VPN gateway is protected from attacks, but the administrator has to additionally configure the firewall to pass encrypted traffic. Gateway functions can be implemented directly on the firewall.
In a separate method, the gateway and the firewall have their own connection with the public IP-network. When agreeing to provide a certain level of quality, the recommendation of the International Telecommunication Telecommunication Union is used. The recommendation provides for three models: 1) “point - many points”; 2) "point - point"; 3) "many points - a point."
To ensure safe operation, a firewall (Firewall), which is part of Windows 7 Enterprise, will be used. A firewall is a software package that checks data coming in through the Internet or a network, and, depending on the settings of the firewall, blocks them or allows them to get into the computer.
A firewall can help prevent hackers or malicious software (such as worms) from entering your computer over the network or the Internet. A firewall also helps prevent malware from being sent to other computers. Figure 10 shows the operation of the firewall.

Figure 10 - Software-based technical method
In order to organize a virtual private network between the two offices of the company, you need to decide on a company that would provide us such a service. At the moment, there are three main communication operators that provide connection to the global information network: Arkhangelsk Television Company (ATK), North-West Telecom (Vanguard), Sovintel (Bee Line).
We will use the services of the ATC, as this company provides good communication quality, the use of Ethernet technology when connecting, powerful channel bandwidth up to 100 Mbps, as well as the ability to increase channel bandwidth without additional costs for the purchase of additional equipment, which is in our case is important. It should be noted that the traffic inside the corporate network is completely free. ATK uses the PPPoE protocol, which provides additional features such as authentication, data, encryption.
PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet) - a network protocol for the data link layer of PPP frames over Ethernet. Mainly used by xDSL services
The PPPoE network protocol is a tunneling protocol that allows you to configure (or encapsulate) IP, or other protocols that are layered on PPP, through Ethernet connections, but with the software features of PPP connections, and therefore it is used for virtual “calls” to a neighboring Ethernet machine and establishes a point-to-point connection, which is used to transport IP packets, working with PPP capabilities. This allows you to use traditional PPP-oriented software to configure the connection, which does not use a serial channel, but a packet-oriented network (like Ethernet) to organize a classic connection with a login, password for Internet connections. Also, an IP address on the other side of the connection is only assigned when the PPPoE connection is open, allowing dynamic use of IP addresses.
5. Summary statement of equipment
local network project topology
During the design process, we determined the necessary volumes of hardware and software. To build the local network of the enterprise, we determined the necessary amount of personal computers, network equipment, and a firewall. All necessary equipment is given in table 3, which is the basis for the feasibility study of the project. The main software is given, respectively, in table 4.
Table 3 - Basic equipment
Table 4 - Basic software
6. Calculation e t access time to the station to the network
To build a local area network in the second office, category 5 twisted-pair cable will be required. For the second office, 200 meters (based on the size of the building) of the cable with a small margin will be required.
A packet, as a rule, has to wait for the right moment in network traffic before it can be transmitted. This time is called the access time and represents the interval until the transmission channel becomes free.
Assume that the retention time of the marker station is (Tud.) 1ms. Considering that in our network in the second office there are 10 workstations (Vnets), then the station access time (Tavt.) Can be calculated by the formula:
T ext. \u003d T beats * V network.
In our case, the retention time was 0.1 second.
Conclusion
As a result of the course work, a local area network was organized in each of the offices. The choice of the main topology was justified, based on standard varieties and technologies that correspond to all modern standards of information transfer.
The parameters of the workstations and the server, the composition of the necessary network equipment, the characteristics of the network equipment, and the network management method were determined. The basic standards of wireless data transmission were studied, and security levels were described, the most optimal for our case was selected.
The choices of data transmission technology and the physical transmission medium were justified. We also identified the main connection devices and their characteristics. Finally, a summary sheet of equipment and programs was determined, in which the necessary amount of personal computers, network equipment was determined. The average access time to the network station was also calculated.
As a result of the course work done, a virtual private network was organized in geographically distributed offices. A virtual private network is provided by the telecom operator, which requires additional costs for payment, but at the same time allows not to build this network in the city. The result is also a complete development and definition of equipment, software. An analysis was made of the level of security, as well as the means that will ensure this security.
List of sources used
1. Roslyakov, A.V. Virtual private networks. - Moscow: Eco-trade, 2006.2. Olifer, V.G., Olifer, N.A. Computer networks. Principles, technologies, protocols. - St. Petersburg: Peter, 2001.3. The site of electronic maps Yandex. Access mode: http: //maps.yandex.ru4. European standard EN 50173-1.5. Standards of the IEEE 802.x.6 family. Site of the Arkhangelsk Television Company (ATK). Access mode: http: //www.atknet.ru7. Microsoft website. Access Mode: http://windows.microsoft.com
At the production of LLC Order, a local connection of computers is used. Local Area Network, hereinafter referred to as LAN, is a combination of computers and other computer equipment (active network equipment, printers, faxes, modems, etc.) connected to a computer network using cables and network adapters and running a network operating system. Computing networks are created with the aim of sharing common network resources (disk space, printers, modems and other equipment), working together with common databases, reducing unnecessary and interfering indoor movements. Each computer in the network is equipped with a network adapter, the adapters are connected using e6n5k4 network cables or wireless technologies and thereby integrate computers into a single computer network. A computer connected to a network is called a workstation or server, depending on their functions.
General provisions of the local network
This Regulation describes the composition and structure of the local network of LLC Order, establishes the principles of using the network services and maintaining databases, as well as information security rules.
1. Definition of terms
The following interpretation of terms and concepts is used in this Regulation:
Local Area Network (LAN) - a hardware-software complex that includes computers, printers, communication equipment, cable system and network operating systems, designed for the efficient use of computing and communication resources of equipment and software.
Drug Administration - Deputy. directors for management and staff of the information and information center
Network operating system - a software component of a LAN designed to manage its parts and resources. Several LAN operating systems can function in a LAN. Depending on the type of system, its components are either located on a separate computer, or distributed across several computers that are part of the LAN.
LAN resources - the computing power of the components of LAN computers, their disk space, network printers, network services used collectively.
A server is a functional part of a network operating system that performs the functions of monitoring and distributing a certain resource.
A computer that performs the function of a server on a network is called this server.
(A computer that performs the function of storing and sharing access to files is called a file server. A computer that implements the function of remote access to LAN is called an access server, etc.).
Main file - server - A dedicated dedicated shared server for college students and teachers.
LAN station - a computer (workstation) included in the LAN through which the LAN user gains access to its resources.
LAN user - an entity that is able to access LAN resources through authorization.
Activ directory is the information structure of a network operating system that authorizes a user and determines the set of his rights and privileges when accessing LAN resources.
IVC employees - authorized employees who perform network management functions and are responsible for its proper operation.
Data archive - a separate section of the file server file system, designed to store data of large volumes and (or) increased responsibility.
Database is an information system that allows you to effectively store, enter, correct and present information, for this purpose structuring information and organizing its management.
Backup - a copy of data intended for backup recovery purposes.
2. The composition and structure of drugs
The main active components of drugs are:
Servers
Specialized network equipment;
Cable system;
Workstations of drugs.
3. Servers
The following main types of servers function as part of the LAN:
LAN file servers
DNS server
DHCP server
Terminal servers
Database servers
Collective use software operates on the terminal servers of the drugs; on the file servers and database servers, respectively, are the personal folders of students and databases.
File servers, communication equipment, database servers, terminal servers are located in specially equipped rooms with limited access.
3.1 Specialized networking equipment
Specialized network equipment is located in a special room with an artificial microclimate and limited access.
3.2 LAN workstations
IBM-compatible computers with a processor no lower than Pentium 4 and having a network interface are used as LAN workstations. The power supply of the LS station is carried out from a separate electrical network that has grounding. The room in which the workstation is located meets the requirements for the placement of electronic equipment.
3.3 Drug operation
Network centers, LAN file servers, access servers work around the clock 7 days a week minus the time for prevention.
4. Customers
Each LAN user must have a name and password authorizing him in the LAN to access the LAN resources.
All students and college teachers are connected to drugs. As a rule, for each group of students included in the LAN, a group client is created on the LAN servers. The network administrator determines the circle of persons entitled to work on the network, tells them the client name and password. The scope of rights of group clients is determined and established by the administrator of the drug.
5. Service functions of drugs
5.1 Data archives
On the main LAN file server for each user, a personal folder is allocated for storing user files. They can be stored results of information systems, other documents. It is forbidden to store computer games, document files that are not related to the implementation of the educational process on LAN servers. The administration of drugs quarterly analyzes the contents of file servers.
Administration of the LAN provides access (copying) to files or folders (files or folders) of students' data to other students only by written (oral) permission of the folder owner.
5.2 Databases
On the LAN servers, databases of information systems for individual use are installed (in particular, 1C, FoxPro 9).
6. LAN and database management
6.1 General coordination of drug use
Responsibilities for the overall coordination of work on the use of drugs subordinate to the deputy. Director for UPR Yakimenko V.K., its development, maintenance, the organization of network management is carried out by the College's ITC.
6.2 Drug Administration
Network management is carried out by the administration of drugs.
Administration of the local network of the structural unit is carried out by the employees of the ITC.
Administration of drugs consists of:
lAN administrator - managing the operation of LAN servers; PM engineers - providing coordination of work on the functioning of hardware and software; laboratory assistant - providing auxiliary functions for drugs.
Functions and responsibilities are fixed in the job description.
6.3 Routine maintenance and maintenance
6.3.1 Data archiving
Data archiving is carried out by system administrators of servers. The system administrator of the server is responsible for data recovery in the event of an accident or malfunction of information systems. Data can be archived daily, weekly, monthly, depending on the type of archived information on schedule.
When significant changes are made to the directory structure of the LAN servers, the creation of new clients, but at least once a month, the main servers archive the system information and directory structure.
Kits of removable media with archives are stored in a sealed safe, the keys to which are located only at the chief engineer.
6.3.2 Periodic work
In PM, work is constantly being carried out to maintain equipment in working condition.
6.3.3 Non-periodic work
Non-periodic scheduled maintenance is carried out according to the plan developed by the administrator of the drug. They may include reconfiguring the network, installing network operating systems, creating virtual networks, and other scheduled maintenance, the need for which is determined by the LAN administration. The calendar part of the scheduled maintenance plan is agreed upon by the administrator of the drug with the deputy. Director for UPR Yakimenko V.K. Non-periodic routine maintenance is recorded in the routine maintenance journal.
6.4 Reporting
For documenting the resources of a medicine, its configuration, ways of accessing its resources, ensuring security, and effectively managing information resources, the administration of drugs conducts the following reports: a map of the topology of drugs; server passport; station card; routine maintenance journal. The map of the topology of the LAN is a floor plan of the LAN with the cabling lines indicated on them, the location of the servers, network centers, other active equipment, the layout of the connected stations and their characteristics. The server passport includes a description of the technical characteristics of the computer and network cards; name and version of the network operating system; the number of possible simultaneously working clients; Network server name Server network address list of software products and information systems installed on the server (name, version). In a separate section of the passport, breakdowns and malfunctions that occurred on the server are recorded.
The server passport is compiled and maintained by the system administrator. It is possible to maintain a server passport in electronic form in encrypted form and signed with an electronic signature. Storage of the electronic version of the server passport on the server itself is prohibited. A card of a LAN station includes the type of computer, the name and version of the operating system, the type of network interface, and the location of the station. The station card is filled after the station is connected to the station.
6.5 Network operation in emergency mode
To protect the LAN from power outages, the LAN servers and network centers are equipped with uninterruptible power supplies, the power of which in the event of a power outage provides at least the ability for users to correctly complete tasks, exit the network and stop the server.
Hard disk drives with a total volume of 20% of the functioning disk space of the main servers. In case of possible emergency situations, the drug administrator develops detailed action plans for the drug administration. Plans should provide for the restoration of network performance in the technologically shortest possible time.
6.6 Responsibility of the administration of drugs
The access of drug administration officials to the information circulating in the network is determined by technical and technological necessity. Drug administration officials are prohibited from misuse of the information to which they gain access in connection with the performance of their functions. All drug administration officials give non-disclosure obligations for information circulating on the network, as well as information on the topology, composition, equipment of the drug, accepted protection rules, passwords, composition, network names and user rights, and other technological and technical information. The administration of drugs is administratively responsible for the strict implementation of the requirements of this Regulation, other regulatory and technical regulations governing the operation of the network, for the uninterrupted and reliable operation of drugs.
7. Safety Rules
7.1 Computer viruses
The Administration of Medicines is obliged to take all necessary technological and organizational-technical measures to prevent the penetration of computer viruses into medicines. For this purpose, specialized anti-virus software is installed. In addition, before moving files from various storage media to the data archive, it is imperative that the user checks these media for viruses. All email is also automatically scanned on the main email server. In case of forced completion of the anti-virus scan, the user is administratively responsible for possible “infections” of viruses. The chief administrator of the drug is developing emergency plans for the administration of the drug in case of a viral "infection" of the network.
7.2 Restrictions on user actions
For each client, the LAN system administrator sets a number of restrictions.
Users are prohibited from informing third parties about the customer names and passwords known to them, or attempting to gain unauthorized access to drug resources. Upon completion of network tasks, the user must exit the network in order to free up network resources.
7.3 Qualification requirements for users
Before receiving a network name and password, the LAN user must know:
general device of a personal computer and the purpose of its main parts;
rules for turning on and off the personal computer and peripheral equipment connected to it, safety rules when working on a personal computer; general principles: work with the user shell of the operating system installed on this personal computer.
7.4 User Responsibility
For violation of the requirements of this provision and the instructions for using a PC, disciplinary sanctions are applied to users of GOU SPO NEPK connected to drugs. Penalties are imposed by the immediate supervisor, whose competence includes the imposition of penalties, on the proposal of the Drug Administration.
7.5 Requirements for equipment included in the network
Equipment included in drugs is equipment that, during normal operation, can affect the information flows and control flows of drugs. Equipment is connected to drugs exclusively by drug engineers. The equipment must comply with the design documentation for the drug. Requirements for the type of equipment and technical characteristics are determined by the Administration of Medicines.
Network passport
1. General characteristics
· Location: LLC “Order”
· Network Name: ORDER.LOCAL
· Network Status: Corporate Network
· Network Purpose: Educational
· Number of servers:
Domain controller, file server: 1
File server: 1
Terminal Servers: 2
Proxy server: 1
· Number of display classes: 6
· Number of workstations: 77
· Number of office computers serving the local network: 3
· Internet connection: ADSL modem
2. Network Settings
Data rate
· For data transfer between network servers and switches, lines with a data transfer rate of 1 Gb / s are used
· For data transmission to network workstations from switches, lines with a data transfer rate of 100 Mb / s are used
Types of information transmitted
· Data required for terminal mode operation via RDP
· User data (files) via TCP / IP
Number of Network Subscribers
· The network consists of 77 workstations, running 4 servers.
· There is an Internet gateway
Network elements
AT8326GB Switch (# 4)
AT-GS908GB Switch
ZyXEL OMNI ADSL LAN Modem
Hub Compex PS2216
Hub Compex DS2216
3. Security
To ensure network security, the following set of programs is used:
· Internal settings of modems and switches
At workstations, protection is provided using special user profiles and terminal shells that restrict access to system settings. Access to BIOS settings is password protected.
4. Backup
To save backup copies of system disks of servers and workstations, user data, the Acronis True Image program is used.
Backups of system disks and user data are stored on all servers on the network.
PRACTICAL PART
Formulation of the problem
When I went through internship at Order LLC, I was given the task of developing an inventory accounting application. Here, as in many enterprises, there is a warehouse where certain work is carried out.
Each company, institution at least once a year before preparing financial statements must conduct an inventory of its own assets and liabilities. Since this topic is always relevant, in this article we will consider the main essential aspects of conducting an inventory of non-budget organizations.
An inventory is a check of the property and liabilities of an organization by counting, measuring, weighing. It is a way to refine accounting indicators and subsequent control over the safety of the property of the organization.
To ensure the reliability of accounting data and financial statements, organizations are required to conduct an inventory of property and liabilities, during which their presence, condition and assessment are checked and documented.
All property of the organization, regardless of its location, and all types of financial obligations, are subject to inventory.
Depending on the extent of verification of property and liabilities, organizations distinguish between full and partial inventories. A complete inventory covers all types of property and financial obligations of the organization, without exception. Partial covers one or more types of property and liabilities, for example, only cash, materials, etc.
Also, inventories are planned and sudden.
The procedure (the number of inventories in the reporting year, the dates of their conduct, the list of property and liabilities checked at each of them, etc.) of the inventory is determined by the head of the organization, unless the inventory is necessary. Cases of mandatory inventory:
Transfer of property for rent, redemption, sale, as well as the transformation of a state or municipal unitary enterprise;
Preparation of annual financial statements (except for property, the inventory of which was carried out not earlier than October 1 of the reporting year). An inventory of fixed assets can be carried out once every three years, library funds - once every five years;
Change of materially responsible persons;
Identification of theft, abuse or damage to property;
Cases of natural disaster, fire or other emergency situations caused by extreme conditions;
Reorganization or liquidation of the organization;
Other cases
The objects of the inventory are: fixed assets, intangible assets, financial investments, inventories, finished goods, goods, other inventories, cash, other financial assets, payables, bank loans, loans, reserves.
To conduct an inventory in the organization creates a permanent inventory commission. The commission includes representatives of the administration of the organization, employees of the accounting service, other specialists (engineers, economists, technicians, etc.). The commission may include representatives of the organization’s internal audit service, independent audit organizations.
Prior to checking the actual availability of property, the inventory committee should receive the latest at the time of the inventory receipt and expenditure documents or reports on the movement of material assets and cash.
Before the inventory carry out preparatory measures. Material values \u200b\u200bare sorted and stacked according to names, grades, sizes; in storage places labels with quantity, mass or measure of checked values \u200b\u200bare posted. all documents on the receipt and expenditure of values \u200b\u200bshould be processed and recorded in the registers of analytical accounting. Prior to the beginning of the inventory, a receipt is taken from each person or group of persons responsible for the preservation of values. The receipt is included in the heading of the form — an inventory list or inventory act, which records information about the actual availability of property and the reality of recorded financial obligations.
Each inventory (act) is compiled in at least two copies and is documented in a uniform form. Forms are mandatory for use by organizations of all forms of ownership. In table 1 you can see the names of the forms and their numbers.
The head of the organization must create conditions that ensure a complete and accurate verification of the actual availability of property on time.
Based on the task, the database should contain:
Item Number;
Name of product;
Unit of measure;
Quantity (in fact);
Amount (upon)
Quantity (after accounting);
Amount (after accounting);
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Posted on http://www.allbest.ru/
BASIC CONCEPTS
Local Area Network - a computer network that usually covers a relatively small area or a small group of buildings (home, office, company, institute). There are also local networks, the nodes of which are geographically spaced at distances of more than 12,500 km (space stations and orbital centers)
Network topology - a way to describe the network configuration, the layout and connection of network devices.
Network topology can be:
Physical - describes the actual location and communication between network nodes.
Logical - describes the signal circulation within the framework of physical topology.
Information topology - describes the direction of information flows transmitted over the network.
Exchange management is the principle of transferring the right to use the network.
Switch - a device designed to connect several nodes of a computer network within the same network segment. Unlike a hub, which distributes traffic from one connected device to all the others, the switch transfers data only directly to the recipient, with the exception of broadcast traffic to all nodes of the network. This improves network performance and security, eliminating the need for other segments of the network (and the ability) to process data that was not intended for them.
The switch operates on the channel 2 layer of the OSI model, and therefore, in the general case, it can only combine the nodes of the same network by their MAC addresses.
OSI Models - An abstract network model for communications and network protocol development. Offers a look at a computer network in terms of measurements. Each dimension serves its part of the interaction process. Thanks to this structure, the collaboration of network equipment and software becomes much simpler and more transparent.
An operating system is a set of control and processing programs that, on the one hand, act as an interface between computing system devices and application programs, and on the other hand, are used to manage devices, manage computing processes, efficiently distribute computing resources between computing processes and organize reliable computing. This definition applies to most modern general purpose operating systems.
Network interface - a connection point between a user's computer and a private or public network
A DHCP server is a network protocol that allows computers to automatically obtain the IP address and other parameters necessary to operate on a TCP / IP network. This protocol works according to the client-server model. For automatic configuration, the client computer at the stage of configuration of the network device accesses the so-called DHCP server and receives the necessary parameters from it. The network administrator can specify the range of addresses distributed by the server among computers. This avoids manual configuration of network computers and reduces errors. DHCP is used on most large (and not so) TCP / IP networks. DHCP is an extension of the BOOTP protocol that was previously used to provide diskless workstations with IP addresses when they boot. DHCP maintains backward compatibility with BOOTP. The DHCP protocol standard was adopted in October 1993. The current version of the protocol (March 1997) is described in RFC 2131. The new version of DHCP, designed for use in an IPv6 environment, is called DHCPv6 and is defined in RFC 3315 (July 2003). DHCP provides three methods for distributing IP addresses:
Manual distribution. With this method, the network administrator maps the hardware address (usually the MAC address) of each client computer to a specific IP address. In fact, this method of address allocation differs from the manual configuration of each computer only in that the address information is stored centrally (on the DHCP server), and therefore it is easier to change if necessary.
Automatic distribution. With this method, each computer is allocated a permanent IP address from the range specified by the administrator for constant use.
Dynamic allocation. This method is similar to automatic distribution, except that the address is issued to the computer not for permanent use, but for a certain period. This is called a rental address. After the lease expires, the IP address is again considered free, and the client must request a new one (it, however, may turn out to be the same).
In addition to the IP address, DHCP can also provide the client with additional parameters necessary for normal network operation. These options are called DHCP options. A list of standard options can be found in RFC 2132.
Some of the most commonly used options are:
The default IP address of the router
Subnet mask;
DNS server addresses
DNS domain name.
Some software vendors may define their own additional DHCP options. DHCP is a client-server protocol, that is, a DHCP client and a DHCP server participate in its work. Data is transmitted using the UDP protocol, while the server receives messages from clients on port 67 and sends messages to clients on port 68. Some DHCP service implementations are able to automatically update DNS records corresponding to client computers when new addresses are allocated to them. This is done using the DNS update protocol described in RFC 2136.
FIREWALL - a complex of hardware or software that monitors and filters the network packets passing through it at various levels of the OSI model in accordance with the specified rules.
IPFW is a firewall that has been built into FreeBSD since version 2.0. With it, you can, for example, calculate traffic according to any reasonable rules based on the data of the packet headers of the TCP / IP stack protocols, process packets with external programs, and hide the whole network at one computer.
VLAN - (Virtual Local Area Network) is a group of hosts with a common set of requirements that interact as if they were connected to a broadcast domain, regardless of their physical location. A VLAN has the same properties as a physical local area network, but allows end stations to group together even if they are not on the same physical network. Such a reorganization can be done based on software instead of physically moving devices. On Cisco devices, VTP (VLAN Trunking Protocol) provides VLAN domains to simplify administration. VTP also purges traffic by directing VLAN traffic to only those switches that have target VLAN ports (VTP pruning function). Cisco switches primarily use the ISL (Inter-Switch Link) protocol to ensure information interoperability. By default, each switch port has a management VLAN1 or management VLAN. The management network cannot be removed, however additional VLANs can be created and ports can be additionally assigned to these alternative VLANs. Native VLAN is a parameter of each port that determines the VLAN number that all untagged packets receive.
A media converter is a device that converts a signal propagation medium from one type to another. The most common medium for signal propagation are copper wires and optical cables. Also, the medium is called the medium of signal propagation, although it is not such, since air does not directly participate in the propagation of high-frequency electromagnetic waves.
A multiplexer is a device that allows, using light beams with different wavelengths and a diffraction grating (phase, amplitude), to transmit several different data streams simultaneously on the same communication line.
FreeBSD is a free Unix-like operating system, a descendant of AT&T Unix from the BSD line created at the University of Berkeley. FreeBSD runs on x86 PC-compatible systems, including Microsoft Xbox, as well as DEC Alpha, Sun UltraSPARC, IA-64, AMD64, PowerPC, NEC PC-98, ARM.
VPN network is a logical network created on top of another network, for example, the Internet. Despite the fact that communications are carried out over public networks, using unsafe protocols, encryption creates channels of information exchange that are closed to outsiders. VPN allows you to combine, for example, several offices of the organization into a single network using uncontrolled channels for communication between them.
A web server is a server that accepts HTTP requests from clients, usually web browsers, and gives them HTTP responses, usually along with an HTML page, image, file, media stream or other data. Web server is called as software that performs the functions of a web server, and directly the computer
MySQL is a free database management system (DBMS). MySQL is owned by Oracle Corporation, which acquired it along with Sun Microsystems, an acquired company that develops and maintains the application. Distributed under the GNU General Public License and under its own commercial license, to choose from. In addition, developers create functionality by order of licensed users, thanks to such an order, a replication mechanism appeared in almost the earliest versions.
PhpMyAdmin is an open source web application written in PHP and representing a web interface for administering MySQL DBMS. phpMyAdmin allows you to administer a MySQL server through a browser, run SQL commands, and view the contents of tables and databases. The application is very popular among web developers, as it allows you to manage the MySQL DBMS without directly entering SQL commands, providing a friendly interface.
A mail server is a computer program that transmits messages from one computer to another. Typically, the mail server works behind the scenes, and users are dealing with another program - the email client (English user agent, MUA).
Exim is a messaging agent used on Unix family operating systems. The first version was written in 1995 by Philip Hazel for use as a postal system at the University of Cambridge. Exim is licensed under the GPL, and anyone is free to download, use and modify it.
SNMP is a communication network management protocol based on the TCP / IP architecture. Based on the TMN concept in 1980-1990. various standardization bodies have developed a number of protocols for managing data transmission networks with a different spectrum of TMN functions implementation. One type of such management protocol is SNMP. Also, this technology is designed to provide management and control of devices and applications in the communication network by exchanging management information between agents located on network devices and managers located at control stations. SNMP defines a network as a collection of network management stations and network elements (host machines, gateways and routers, terminal servers) that together provide administrative communications between network management stations and network agents.
Cacti is an open-source web application, the system allows you to build graphs using RRDtool. Cacti collects statistics for specific time intervals and allows you to display them in graphical form. Mostly standard templates are used to display statistics on processor loading, RAM allocation, the number of running processes, and the use of incoming / outgoing traffic.
IP Pool - a collection of consecutive IP addresses within the TCP / IP computer network.
A proxy server is a service on computer networks that allows clients to perform indirect requests to other network services. First, the client connects to the proxy server and requests a resource (for example, e-mail) located on another server. Then the proxy server either connects to the specified server and receives the resource from it, or returns the resource from its own cache (in cases where the proxy has its own cache). In some cases, a client request or server response may be modified by the proxy server for certain purposes. Also, a proxy server allows you to protect the client computer from some network attacks.
MPLS is a data transfer mechanism that emulates various properties of circuit-switched networks on top of packet-switched networks. MPLS operates at a level that could be located between the second (channel) and third (network) layers of the OSI model, and therefore it is usually called the second and a half layer protocol (2.5 level). It was developed with the aim of providing a universal data transfer service for both clients of circuit-switched networks and packet-switched networks. Using MPLS, you can transfer traffic of a wide variety of nature, such as IP packets, ATM, Frame Relay, SONET, and Ethernet frames.
FTP is a protocol for transferring files on computer networks. FTP allows you to connect to FTP servers, view the contents of directories and upload files from or to a server; In addition, a file transfer mode between servers is possible. FTP refers to application layer protocols and uses the TCP transport protocol for data transfer. Commands and data, unlike most other protocols, are transmitted on different ports. Port 20 is used for data transmission, port 21 for command transmission. If the file transfer was interrupted for any reason, the protocol provides means for downloading the file, which is very convenient when transferring large files. The protocol is not encrypted; during authentication, the login and password are transmitted in clear text. In the case of building a network using a hub, an attacker using a passive sniffer can intercept the logins and passwords of FTP users located in the same network segment, or, in the presence of special software, receive FTP files transmitted without authorization. To prevent traffic interception, you must use the SSL data encryption protocol, which is supported by many modern FTP servers and some FTP clients. Initially, the protocol involved an oncoming TCP connection from server to client to transfer a file or directory contents. This made it impossible to communicate with the server if the client is behind IP NAT, in addition, often the connection request to the client is blocked by a firewall. To avoid this, an extension of the FTP passive mode protocol was developed when a data connection also occurs from the client to the server. The important point is that the client establishes a connection with the address and port specified by the server. The server selects a port randomly from a certain range (49152-65534). Therefore, when finding the ftp server behind NAT, you should explicitly specify its address in the server settings.
Server Rack - is a universal floor rack for mounting 19 inch.
A patch panel is one of the components of a structured cabling system (SCS). It is a panel with many connectors located on the front side of the panel. On the rear side of the panel there are contacts designed for fixed connection with cables and electrically connected to the connectors. The patch panel refers to passive network equipment.
SCS is the physical basis of the information infrastructure of the enterprise, which allows you to bring together a multitude of information services for various purposes into a single system: local computer and telephone networks, security systems, video surveillance, etc.
POP3 server - used by the mail client to receive email messages from the server. Commonly used in conjunction with the SMTP protocol.
IMAP server is an application layer protocol for accessing email.
Like POP3, it is used to work with incoming letters, but it provides additional functions, in particular, the ability to search by keyword without saving mail in local memory. IMAP provides the user with extensive options for working with mailboxes located on a central server. A mail program using this protocol gains access to the correspondence repository on the server as if this correspondence is located on the recipient's computer. Emails can be manipulated from the user's computer (client) without constantly sending files with the full contents of the letters from the server and back.
NAT from English. Network Address Translation is a mechanism in TCP / IP networks that translates the IP addresses of transit packets. Also named IP Masquerading, Network Masquerading and Native Address Translation. Address translation using NAT can be done by almost any routing device - a router, access server, firewall. The most popular is SNAT, the essence of the mechanism of which is to replace the source address (source) when the packet passes in one direction and reverse the destination address (destination) in the response packet. Along with the source / destination addresses, the source and destination port numbers can also be replaced. In addition to source NAT (providing users with a local network with internal Internet access addresses), destination NAT is also often used when external calls are transmitted by a firewall to a server on the local network that has an internal address and therefore is not directly accessible from the outside (without NAT). There are 3 basic concepts of address translation: static (Static Network Address Translation), dynamic (Dynamic Address Translation), masquerade (NAPT, NAT Overload, PAT):
Static NAT - Mapping an unregistered IP address to a registered IP address on a one-to-one basis. Especially useful when the device should be accessible from outside the network;
Dynamic NAT - Displays an unregistered IP address to a registered address from a group of registered IP addresses. Dynamic NAT also establishes a direct mapping between an unregistered and a registered address, but the mapping may vary depending on the registered address available in the address pool during communication;
Congested NAT (NAPT, NAT Overload, PAT, masquerade) is a form of dynamic NAT that maps multiple unregistered addresses to a single registered IP address using different ports. Also known as PAT (Port Address Translation);
The kernel (FreeBSD) is the main part of the FreeBSD operating system. It is responsible for memory management, security settings, networking, disk access, and more.
MAIN GOALS
The aim of the thesis is to consider the principle and approach to building a corporate local network using the example of a network of a commercial enterprise of a large commodity producer.
In the thesis, the following important points are considered:
Architecture, construction and data transmission method;
Access method, topology, type of cable system;
Choosing a network management method;
Network equipment configuration - the number of servers, hubs, network printers;
Management of network resources and network users;
Network Security Considerations
local area network
Physical network topology enterprises
The enterprise network consists of four offices, two of which are remote points. Each of which has its own physical data transfer.
Office equipment 4
To understand the physical topology of office 4, consider a diagram.
Office 4 used the following physical media:
1) according to MPLS technology (ADSL) between the main office and office 4, the transmission and reception speed is 128/64 Kbit / s .;
2) the optical transmission medium between the ADSL modem and the DLink switch, since there is a distance of 340 m between them and the maximum allowable length using Ethernet technology is not more than 100 m;
3) Ethernet data transmission medium between the DLink switch and personal computers connected to the switch via an Ethernet cable.
At office 3, a physical data channel is connected at a speed of 1 Mb / s using Ethernet technology.
Office equipment 3
To understand the physical topology of office 3, consider a diagram.
Office 3 uses two physical media:
1) Wi-Fi (from a PC or end-client equipment to a wireless access point);
2) Ethernet environment (from a wireless point to a DLink DIR-100 router and beyond)
Office 2 equipment
|
Name |
|||
|
Switch managed by DLink 8 ports |
|||
|
Single-mode media converters (one working fiber, second spare) |
|||
|
DLink 24 Port Unmanaged Switches |
|||
|
Wi-Fi dot DLink |
|||
|
Office pc |
|||
|
Optical boxes |
|||
The diagram shows the physical topology of office 2.
Office 2 used the following physical media:
1) an optical data transmission medium between office 2 and the main office: by converting the Ethernet data transmission medium into an optical medium through a pair of media converters into an optical data transmission medium between office 2 and the main office;
2) Physical data transmission medium in the middle of office 2, topology “star” Ethernet technology;
3) Wireless data transmission medium (from PC to access point)
Office 1 or the main node.
In principle, the construction of the corporate network of the enterprise laid down the principle of centralization. All main switching, connections and the central rack are located in the server room of the main office.
Office equipment 1
|
Name |
|||
|
Rack central Conteg 19 ”21U |
|||
|
Universal patch panels for SCS |
|||
|
Switch 3Com 4200 Super Stack 50 ports |
|||
|
Single-mode media converters |
|||
|
Optical boxes |
|||
|
Personal computers, network printers and IP cameras |
|||
|
Multiplexer |
|||
|
Optical 4 fiber cable |
|||
|
AP Access Point DLink 2100 AP |
The diagram shows the following physical media:
1) optical data transmission medium between the main office and office 2: by converting the Ethernet data transmission medium through a pair of media converters into an optical data transmission medium between office 2 and the main office;
2) The physical transmission medium in the middle of the main office is the star topology according to the SCS project, Ethernet technology;
3) Wireless transmission medium.
The logical structure of the enterprise network
The entire enterprise network is built on the principle of using VLAN technology.
The total number of VLAN networks is 7 networks.
Enterprise networks based on VLAN technology
|
The name of the virtual network |
Accommodation |
|||
|
Main office |
||||
|
Main office |
||||
|
Vlan 5 - pool of IP addresses |
81.90.232.144/28 |
Main office |
||
|
Vlan 6 - pool of IP addresses |
Main office |
|||
To understand the logical structure of the entire network, consider a diagram. For convenience, we will first consider the logical structure of each office, and then the interaction of all offices with the main one.
Logical structure of the main office network
1) The first server in the diagram is a server based on the FreeBSD OS. It performs the following roles:
Router with reservation of Internet channels;
Service for VLAN subnets;
NAT service;
VPN server
SMTP server;
Squid proxy server;
POP3 server and IMAP;
Web server
MySQL server;
DHCP server
The FreeBSD server is the default gateway for all vlan networks. He plays a major role in building an enterprise network.
5 tagged vlans, the 3Com Super Stack 4200 switch opens up for users in open form for 4 networks of the main office and 1 network of the office 4;
2 tagged Vlan 3Com Super Stack 4200 transmits in a closed form through an optical transmission medium to a managed DLink switch;
3) To manage and control the networks of 5 networks of the main office, a server based on the Windows 2003 Server Standart R2 OS located on the vlan3 network was selected into one logical unit. It performs the following functions:
Active Directory Server
Terminal server;
DNS server
All users of the main office and office 4 networks are registered in the TD-OLIS main office domain.
4) A database server with a business system that is part of the TD-OLIS domain. Located on the vlan3 network.
5) Server of security of telephone conversations and recording of telephone calls located on the vlan3 network
The FreeBSD server is not part of the TD-OLIS domain.
Logical structure of office network 2
To manage and control 2 networks of Office 2, a server based on the Windows 2003 Server Standart R2 OS was selected in one logical unit. It performs the following functions:
Active Directory Server
Terminal server;
DNS server
Office 2 has its own database server with a business system and does not overlap while working with the database server of the main office.
All users of 2 networks of office 2 are registered in the OLIS domain.
Since the server based on the Windows 2003 Server Standart R2 OS is the main server for office 2, the main traffic between the hosts of office 2 and it is:
Udp, \u200b\u200bport 53- since our server is a domain holder;
Logical structure of office network 4
Office 4 is the logical part of the main office of the vlan7 network thanks to MPLS technology.
The main traffic for office 4 is:
Logical structure of office network 3
Office 3 is a separate logical unit with its own local network. The main gateway for office 3 is the DLink DIR-100 router configured with a static real IP address by this provider. All IP traffic passes through the DLink DIR-100. The LAN address in the middle of office 3 is 192.168.100.0/24.
The interaction of the main office and office 2
The interaction of office 2 and the main office:
Office 2 networks - are the main office networks that are transmitted through the optical medium using Vlan technology and managed switches to office 2;
All office 2 traffic goes through the main office to a server running FreeBSD, which is the default gateway for office 2 networks.
The logical interaction of the main office and office 3
To provide secure access to the database server of the main office, the office router 3 DLink DIR-100 is used, which connects to the FreeBSD server using vpn technology, FreeBSD is a PPTP vpn server. Based on the accounts, username and password that the router transmits, an IP address is issued. The FreeBSD server handles vpn connections on port 1723, the tcp protocol. That is, office 3 is part of the vpn network. Access to the database server of the main office is carried out through the RDP protocol, based on the accounts set up in the Active Directory domain server of the main office.
The logical interaction of the main office and office 4
Office 4 is part of the vlan7 network.
Vlan7 network users are registered in the TD-OLIS domain of the main office. The default gateway for vlan7 hosts is the FreeBSD server.
Configuring servers and equipment that supports the operation of the enterprise network
FreeBSD Server
FreeBSD server as a gateway and router
Our server is connected to two Internet channels:
Optical fiber 5Mb / s., Golden Telecom Internet provider with a network of 8 IP addresses;
Optical fiber 5Mb / s., Internet provider "Radiocom" with a network of 8 IP addresses, registered in static routing;
The main channel for the server is the Golden Telecom channel.
Additional services:
The pool of IP addresses from the provider Golden-Telecom for 16 IP addresses registered through a static route;
It turns out that physically we have two ethernet interfaces, on which we must register 8 IP addresses from each provider, and register an additional 16 IP addresses. The server must be the default gateway for all of our subnets.
To achieve this goal, let us modify the main rc.conf configuration file.
The rc.conf file contains descriptive information about the local host name, configuration information for any potential network interfaces, and what services should be operational in the boot system. The rc.conf file is located in the / etc directory.
We are interested in the following options for changing the rc.conf file:
defaultrouter or default router - issued by the Internet provider, in our case, it is a router from Golden Telecom;
gateway_enable - accepts YES or NO, that is, whether our server will be the default gateway or not;
ifconfig_interface - this option is used to configure the physical network interface;
ifconfig_interface_alias0 - to add additional IP addresses to the same physical interface.
In the figure, the rc.conf file after the change.
Figure - the modified rc.conf configuration file with the changes made to enable the functions of the router, gateway, and network interface settings
FreeBSD Server and NAT Service
The FreeBSD OS provides a fairly large number of standard tools for running the NAT service.
In our network, we used the PF complex, which can translate Network Address Translation (NAT) addresses;
Before registering the necessary options in rc.conf, we must recompile the FreeBSD OS kernel with the new necessary options necessary for the OS to support PF Nat at the kernel level.
The main configuration PF is called pf.conf.
The basic NAT rule format in pf.conf is as follows:
nat on interface from src_addr to dst_addr -\u003e ext_addr, where:
1) nat is the keyword with which the NAT rule begins;
2) pass - converted packets will not be processed by filtering rules;
3) log - log packets using pflogd. Usually only the first packet is logged. To log all packets, use log (all);
4) interface - the name of the interface or group of interfaces on which conversions will be performed;
5) af - a family of addresses, inet for IPv4 or inet6 for IPv6. PF, as a rule, is able to determine this parameter by itself using source addresses and destination addresses.
6) src_addr - source (internal) addresses of packets to be converted. Source addresses can be specified as:
Network Block CIDR;
The name of the network interface or group of network interfaces. Any IP addresses belonging to the interface will be substituted as a rule at boot time;
The name of the network interface followed by / netmask (for example, / 24). Each IP address on the interface, combined with a network mask, forms a CIDR block and appears in the rule;
The name of the network interface or group of network interfaces, followed by modifiers:
Broadcast - is replaced by the broadcast address of the network (for example, 192.168.0.255);
In addition, the modifier: 0 can be added to any interface or to any of the above modifiers, to indicate that the PF should not affect alias IP addresses. This modifier can be used when specifying an interface in parentheses. Example: fxp0: network: 0
7) src_port - the source port in the packet header. Ports can be specified as:
Number from 1 to 65535
See the current service name in / etc / services
Port Set Using Lists
Range:
! \u003d (not equal)
< (меньше)
-\u003e (more)
<= (меньше или равно)
\u003e \u003d (greater than or equal to)
>< (диапазон)
<> (reverse range)
The last two binary operators (they use two arguments) do not include arguments in this range
: (including range)
Inclusive range, also binary operators and include arguments in the range.
The port option is not often used in nat rules, because it is usually a task to convert all traffic, regardless of the ports used.
8) dst_addr - destination address of converted packets. Destination address is the same as the source address;
9) dst_port - destination port. The port is specified in the same way as the source port;
10) ext_addr - an external (translatable) address on the NAT gateway into which packets will be forwarded. An external address can be specified as:
A single IPv4 or IPv6 address;
Network Block CIDR;
The fully qualified domain name that will be resolved through the DNS server when the rule is loaded. The received addresses will appear in the rule;
The name of the network interface. Any IP addresses belonging to the interface will be substituted as a rule at boot time;
The name of the network interface indicated in parentheses (). This tells PF to update the rule if the IP address (s) on the specified interface has changed. It is useful on interfaces that receive IP addresses via DHCP or use dial-up so that each time the address is changed, the rules are not overloaded;
The name of the network interface followed by one of these modifiers:
Network - is replaced by the CIDR network block (for example, 192.168.0.0/24);
Peer - peer is replaced by the IP address of the other side of the point-to-point link;
In addition, the modifier: 0 can be added to any interface or to any of the above modifiers, to indicate that the PF should not use alias IP addresses. This modifier can be used when specifying an interface in parentheses. Example: fxp0: network: 0 A series of addresses using a list
11) pool_type - indicates the type of address range used for translation;
12) static-port - do not convert source ports in TCP and UDP packets;
The nat on $ inf1 from 10.0.0.9 to any -\u003e $ ip1 rule says that:
All packets going through the fxp0 interface from the IP address 10.0.0.9 to the world should be broadcast to the world from the IP address 94.27.59.74.
The rule nat on $ inf1 from 10.64.1.0/24 to any -\u003e $ ip1 says that:
All packets going through the fxp0 interface from the network 10.64.1.0/24 to the world should be broadcast to the world from the IP address 94.27.59.74.
In order to verify whether NAT works in a practical way or not, just go to any site that identifies your IP address. In this configuration file, a system of variables and access to variables are introduced. Why this is done will be described in the section
The pass in all and pass out all configuration lines allow traffic to flow in both directions.
When changing the pf.conf configuration file, you must restart pf with the command:
Pfctl -f /etc/pf.conf
FreeBSD as FIREWALL
FreeBSD includes the full-time IPFW firewall. The firewall configuration is set in the form of a list of numbered rules, which is scanned for each packet until a match is found - then the action specified by the corresponding rule is performed. Depending on the action and some settings on the system, packets may be returned to the firewall for processing
rules starting with the one that worked. All rules apply to all interfaces, so the task of writing a set of rules with the minimum required number of checks rests with the system administrator. The configuration always includes the standard rule (DEFAULT) with the number 65535, which cannot be changed and which corresponds to any packet. A deny or allow action may be associated with this standard rule, depending on the kernel configuration.
If the rule set includes one or more rules with the keep-state option, then ipfw assumes work with stateful behavior, i.e. upon successful matching, it will create dynamic rules corresponding to the specific parameters (addresses and ports) of the matched packet. These dynamic rules with a limited lifetime are checked, starting from the first occurrence of the check-state or keep-state rules, and are usually used to open the firewall on demand only for acceptable traffic. An additional opportunity provided by dynamic rules is the ability to limit the number of simultaneous connections corresponding to a rule (this can be useful if you want to deal with "left" proxy servers on your network - a dozen simultaneous connections are enough for the user to work normally, while for a proxy server this amount is clearly insufficient). To limit the connections, add the limit parameter to the "generating" rule, for example:
sbin / ipfw add allow ip from 192.168.0.1/24 to any keep-state limit src-addr 10
prohibits each subscriber of the network 192.168.0.1:255.255.255.0 from establishing more than 10 connections simultaneously. The src-addr parameter indicates that the restriction is calculated according to the addresses of the package sources (i.e., in our example, for each user). Valid values \u200b\u200bfor this parameter are: dst-addr (restriction is calculated by destination address), src-port (restriction is calculated by source port), dst-port (restriction is calculated by destination port), as well as any combination of these parameters, for example, limit dst- port dst-addr 1 will allow you to establish only one connection to any port of any server, while it will be possible to establish several connections to one server (for example, HTTP, SMTP and POP3 at the same time) and several connections to one port of different servers
Speed \u200b\u200bLimit
Firewall allows you not only to allow or prohibit the passage of IP packets, but also to limit the speed of their passage. For this, the dummynet system built into the FreeBSD kernel is used - an emulator of a "bad" communication line with custom characteristics, such as absolute delay in the passage of a packet, limitation of the speed of data transmission along the line, loss of a certain number of packets.
Dummynet consists of pipes (pipe, pipe) and queues (queue). A channel is characterized by bandwidth (bits per second), packet transit delay (in seconds), queue size (how much data can be "located" in a channel at the same time), percentage of losses. You can set these values \u200b\u200busing the command
/ sbin / ipfw pipe<номер> config bw<скорость> delay<время> queue<очередь> plr<процент>
Where<номер> - channel number. It is randomly selected by the administrator from the range 1-65534
<скорость> - channel bandwidth. Set as a number interpreted as bits per second. The task and units of measure from the following set are also possible: bit / s, Kbit / s, Mbit / s, Bytes / s, KBytes / s, MBytes / s. Units are indicated after the number without spaces: 2MBytes / s, 64Kbit / s.
<время> - packet delay time in milliseconds, always added to the time that any packet was in the channel, regardless of the current channel load.
<очередь> - the queue size in packets or in kilobytes (if the units of measurement are specified - Bytes or KBytes). Non-queued packets are discarded.
<процент> - percentage of lost packets. Commonly used to emulate bad communication lines when checking network software resilience to failures. It is set as a real number from 0 to 1 (0 - no losses, 1 - all packets are lost).
To control the channel, you need to imagine how it works - otherwise inconsistencies and unpleasant disappointments are inevitable. When a packet enters the channel, it’s “in the tail” of the queue - just like in a store. Dummynet a certain number of times per second (set by the HZ parameter when assembling the kernel of the operating system) checks for the presence of packets in the queue, and, if the speed limit for exiting the data from the channel is not exceeded, it releases the packet. It is considered that the rate at which packets exit the channel is considered - therefore, if packets arrive at the queue at a higher speed than the exit speed allowed for a given channel, then packets that are not placed in the queue are simply lost.
For the user, if he works over TCP, packet loss is not noticeable - the server stops sending packets if the client does not send an acknowledgment. However, waiting for confirmation for each packet reduces performance - the communication channel can provide greater bandwidth with a sufficiently long packet transit time, and if you wait for a response for each packet, the channel will be idle. Therefore, TCP uses the window method - it sends several packets at once without waiting for confirmation, and sending packets stops only if the confirmation has not yet arrived at the pose-pose-past packet.
In order for TCP to work through the dummynet channel without having to resend the packet, it is necessary that all packets of the window can fit in the queue. The standard queue size (50 packets) is enough for approximately 10 TCP connections to work simultaneously (this number very much depends on the TCP protocol settings on client machines and servers, as well as on the average packet size generated by applications). If this number is exceeded, packets will begin to be lost, which will require re-sending them. If you pay for traffic, this feature can hurt you too much: your provider will count all the packages transferred to your system, including those lost in dummynet, however you (or your client) will receive only part of them - therefore, if you launch a large number of connections through one dummynet channel - increase the queue size proportionally. Moreover, the calculation of the peak number of simultaneous connections is not so simple at all - users with a clamped bandwidth of the channel tend to open much more simultaneous connections than the owners of high-speed channels: while they read one page, they start to download several more. In addition, users of GetRight-type download managers will quickly find that downloading a file into several streams is faster than into one - packets addressed to them, due to their larger number, will “push out” foreign connections from the queue and the duration of one connection will increase, which also will lead to an increase in their simultaneous number.
To configure the queue, use the command:
/ sbin / pfw queue<номер_очереди> config pipe<номер_канала> weight<вес>
queue_number - an identifier arbitrarily chosen by the administrator from the range 1-65534;
channel_number - the number of the channel this queue becomes a part of;
weight - priority of the queue, a number from the range of 1-100, where 100 is the highest priority channel, 1 is the most powerless. By default, priority 1 is set for each queue;
To "pass" traffic through the channel, use the commands:
/ sbin / ipfw add pipe<номер> <правило> or / sbin / ipfw add quqeue<номер> <правило>, eg
Since our server acts as IPFIREWALL, limiting the speed and controlling connections on the ports, consider a real firewall example.
It was previously indicated that the network was created based on VLAN technology. FreeBSD does not use any special programs to create and manage VLANs. Everything is done using the ifconfig program.
Figure - fragment of the rc.conf file where vlan networks are created on the server
Consider this configuration:
line 1 cloned_interfaces creates 6 vlan-interfaces that will create the server during boot and startup;
next, we configure the vlan 1 interface with a line and say that the vlan 1 network with the address 10.0.0.1 with the subnet mask 255.255.255.192 corresponds to this interface and we take any physical interface as the basis for creating vlan, in our case it is the em0 interface;
the physical interface em0 must be registered in rc.conf, any IP address can be assigned to it. But it may not be connected to the network.
FreeBSD Server as a DHCP Server
Our FreeBSD server is a DHCP server for all networks.
In order to configure the FreeBSD system as a DHCP server, you need to ensure the presence of a bpf device compiled into the kernel. To do this, add the line device bpf (pseudo-device bpf in FreeBSD 4.X) to your kernel configuration file.
The bpf device is already part of the GENERIC kernel that ships with FreeBSD, so you don’t need to create your own kernel to enable DHCP.
Those who pay special attention to security issues should note that bpf is the device that allows packet sniffers to work normally (although such programs require privileged access). A bpf device is required to use DHCP, but if you are very concerned about security, you probably do not need to include bpf in your kernel just because you intend to use DHCP in the distant future.
The next step you need to perform is editing the sample dhcpd.conf, which is installed as part of the net / isc-dhcp3-server port. By default, this is the file /usr/local/etc/dhcpd.conf.sample, and you must copy it to the file /usr/local/etc/dhcpd.conf before editing it.
DHCP server setup
dhcpd.conf consists of declarations regarding subnets and hosts, and is most easily described using an example:
option domain-name "example.com";
option domain-name-servers 192.168.4.100;
option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0;
default-lease-time 3600;
max-lease-time 86400;
ddns-update-style none;
subnet 192.168.4.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 (
range 192.168.4.129 192.168.4.254;
option routers 192.168.4.1;
hardware ethernet 02: 03: 04: 05: 06: 07;
fixed-address mailhost.example.com;
This parameter sets the domain that will be issued to clients as the default domain for the search. See the resolv.conf man pages for more information on what this means.
This parameter specifies a comma-separated list of DNS servers that the client should use.
The netmask that will be issued to clients.
The client can request a certain time, which will be issued information. Otherwise, the server will issue settings with this period (in seconds).
This is the maximum time that the server will issue a configuration. If the client requests a longer period, it will be confirmed, but only max-lease-time seconds will be valid.
This parameter specifies whether the DHCP server will try to update DNS when issuing or releasing configuration information. In an ISC implementation, this parameter is required.
This is a definition of which IP addresses should be used as a reserve for issuing to clients. IP addresses between and including boundaries will be issued to clients.
Announcement of the default router to be issued to clients.
The hardware MAC address of the host (so that the DHCP server can recognize the host when it makes a request).
Determining that the host will always be given the same IP address. Note that specifying the host name here is correct, as the DHCP server will resolve the host name on its own before issuing configuration information.
Once you have finished compiling your dhcpd.conf, you can continue by starting the server with the following command:
# /usr/local/etc/rc.d/isc-dhcpd.sh start
If in the future you need to make changes to your server settings, it is important to note that sending a SIGHUP signal to dhcpd will not lead to a reset of settings, as is the case for most daemons. You need to send a SIGTERM signal to stop the process, and then restart it using the command above.
- / usr / local / sbin / dhcpd - dhcpd is configured statically and is located in the / usr / local / sbin directory. The dhcpd (8) help pages set by the port contain more complete dhcpd information;
- /usr/local/etc/dhcpd.conf - dhcpd requires a configuration file, /usr/local/etc/dhcpd.conf, before it starts and starts providing services to clients. It is necessary that this file contains all the data that will be issued to serviced clients, as well as information about the server. This configuration file is described on the help pages that are set by the port;
- /var/db/dhcpd.leases - the DHCP server maintains a database of the issued information in this file, which is written in the form of a protocol. The dhcpd.leases (5) help pages set by the port provide a much more detailed description;
- / usr / local / sbin / dhcrelay - dhcrelay is used in difficult situations when the DHCP server forwards requests from the client to another DHCP server on a separate network. If you need this functionality, then install the net / isc-dhcp3-server port.
FreeBSD Server and RedundancyInternet feeds
As a system for channel reservation, a special Shell script was written.
The shell command language (in translation - shell, shell) is actually a very high level programming language. In this language, the user controls the computer. Usually, after logging in, you start interacting with the shell (if you like, it starts interacting with you). A sign that the shell is ready to receive commands is the prompter issued by it on the screen. In the simplest case, this is one dollar ("$"). Shell is not necessary and the only command language (although it is it that is standardized within the framework of POSIX - the standard for mobile systems). For example, cshell is quite popular, there are also kshell, bashell (of the most popular recently) and others. Moreover, each user can create his own command language. It can simultaneously work with different command languages \u200b\u200bon one instance of the operating system.
Similar documents
Creation of a local area network, its topology, cable system, technology, hardware and software, minimum server requirements. The physical construction of the local network and the organization of Internet access, the calculation of the cable system.
term paper, added 05/05/2010
Functional diagram of a local area network, analysis of information needs and enterprise flows. Network structure planning, network architecture and topology. The structure of the corporate computer network, devices and communications.
term paper, added 08/26/2010
Types of computer networks, their structural elements and subsystems. SCS horizontal subsystem and computer network, local network nodes and distribution points. Server-based network and local area network. Wireless network. LAN: their topology and structure.
abstract, added July 16, 2008
The organizational structure of the enterprise "LEPSE", the composition of network applications. Choosing a Fast Ethernet network configuration, using a star network topology. The structure of the cable system of the organization’s network. Checking the performance of the designed network.
test, added 05/10/2011
Local area network as an association of computers located in a limited space. Analysis of the information needs of the enterprise. Network structure planning: its topology, cable system, equipment used. Calculation of the number of computers.
control work, added 06/22/2014
Computer local area network: design on two floors, the interaction of about 30 machines. The distance between machines and switches is at least 20 meters, the number of switches within the project. Logical and physical network topology.
laboratory work, added 09/27/2010
Services running on the local network. A selection of software. Logical network topology. Physical implementation of a local area network. The layout of server hardware in a 19-inch rack. Ensuring electrical safety and data security.
term paper, added 11/27/2013
Comparative analysis of various network topologies. Study of the elements of a structured cabling system. Access methods and frame formats for Ethernet technology. Shared-Local Area Networks: TokenRing, FDDI, Fast Ethernet.
term paper added 12/19/2014
The structure of the local computer network of the organization. Calculation of the cost of building a local network. Local organization network designed by technology. Building an Ethernet LAN organization. LAN diagram 10Base-T.
term paper, added 06/30/2007
Installation and routing of the LAN 10 Base T. General wiring diagram. Areas of application of computer networks. Information transfer protocols. Network topologies used. Ways to transfer data. Characteristics of the main software.
An enterprise network can be seen as a model of group collaboration, a solution for application software for workgroups. It unites the local network of the branch and the enterprise, is the material and technical base for solving the planning, organization and implementation of its production and economic activities. It provides the functioning of an automated control system and an enterprise information service system. The network structure of the enterprise is given in the appendix.
It highlighted the network equipment located in the central office of the enterprise and in its regional branches. The central office has a local area network (LAN), which includes five personal computers. Through the telephone line and LAN modems, there is access to the territorial communication network of Frame Relay technology, where dedicated telephone lines are used. The same network equipment is available at the regional office. Remote personal computers through the access server and the territorial communication network have direct connection with the LAN of the central office.
The network map includes:
A computer server that can act as an Internet server;
Client computers that have network software that allows you to send and receive packet data over TCP / IP;
Network Operating System (OS) that supports the TCP / IP protocol - Windows NT;
This OS is available in two versions: for a workstation - Windows NT Workstation and in a version for a dedicated server - Windows NT Server. Both OS variants include client and server parts of many network services. Windows NT Workstation, in addition to performing the functions of a network client, can provide network users with a file service, a print service, a remote access service, etc., and therefore, can serve as the basis for a peer-to-peer network. On the other hand, Windows NT Server OS contains all the necessary tools that allow you to use the computer under its control as a client workstation. Under Windows NT Server, it is possible to run application programs locally, which may require the client to perform OS functions when requests for resources of other computers on the network appear. Windows NT Server has the same developed graphical interface as Windows NT Workstation, which makes it possible to use these OSs for interactive work of a user or administrator.
However, Windows NT Server has more opportunities to provide resources of its computer to other network users, as it supports a wider range of functions, more simultaneous connections with clients, centralized network management, and more advanced security features. Therefore, it makes sense to use Windows NT Server as an OS for dedicated servers, not client computers.
Server software that supports browser requests in the format of the protocol for transmitting hypertext messages (HTTP);
Browser software for various client computers (Microsoft Internet Explorer). If you have an Internet connection, Internet Explorer allows you to search and view information on the Internet. To open the desired web page, you can enter its address in the address bar or select from the Favorites list. Internet Explorer also allows you to search the Internet for people, organizations, and information on issues of interest. Thanks to the security features of Internet Explorer, you can be sure that your computer and personal information are safe when browsing the web.
The network is based on client-server technology, i.e. network application is divided into parties:
Customer requesting data or services
Server serving client requests.
Add configuration and description by
| | | next lecture \u003d\u003d\u003e | |
Organization of a computer network of an enterprise. To increase the efficiency and degree of automation of information technology implemented using AWS, the latter should be combined into local networks with outputs to the corporate and global networks. The physical implementation of information technology in enterprise management, as a rule, contains the features of the organizational structure and represents a computer network, divided into segments, the connection between which is via a switching device - bridge Fig. 16 . The administration segment contains the director's workplace and chief specialists.
A server is connected to this segment, where the enterprise data bank and the main functional software are stored.
Fig. 16. Topology of the computer network of a large enterprise. The bus technology of the segment allows data exchange between the chief specialists of the enterprise and the director, and through the bridge to communicate with the AWP of the services of the chief specialists of accounting, planning and economic department, etc. Management decisions are prepared and made in this segment.
The services of the chief specialists are divided into segments and the main specialists' workstations can interact between themselves and across the bridge. On the computers of these segments of the enterprise’s computer network, production plans are developed, accounting and analysis of production parameters are carried out, aggregated information and recommendations on production management for the administration segment are prepared.
Production information characterizing the dynamics of the production process at the enterprise is collected and undergoes primary processing in the segments of production units. The computer network server of the enterprise through the interface device is connected to the trunk channel, giving access to corporate networks and the Internet.
In large enterprises and associations, production units are often removed from the administrative building, which requires communication channels to connect remote segments. For this purpose, a switched telephone network can be used, the data transmission of which is carried out using a modem. In this case, the segments of production units are connected via remote bridges and modems to the telephone network. Either the administrative segment or the bridge of the computer network of the administrative building is connected to it through a modem.
Data transmission over the public telephone network is of low quality and speed. Therefore, to reliably connect segments of production units to the enterprise administration network, it is desirable to have dedicated telephone lines. Stable operation of a computer network is impossible without control. Network management functions are assigned to the network administrator. Its functions include physical and programmatic organization of the network, traffic management, maintenance of network software and equipment.
The process of data accumulation in the enterprise can be implemented by organizing the enterprise data bank on the server and local databases on the workstation. Strategic and tactical data should be stored in the data bank, and operational and informational data should be stored in local databases. 7.
End of work -
This topic belongs to the section:
Types of Translation Transformations
For example, the technology for the production of butter from milk. Technology - a set of processing methods, manufacturing, changes ... The information aspect includes a description of the principles and methods of production, instrumental - tools, using ...
If you need additional material on this topic, or you did not find what you were looking for, we recommend using the search on our database of works:
What we will do with the material received:
If this material turned out to be useful for you, you can save it to your page in social networks:
| Tweet |
All topics in this section:
Information and Information System
Information and information system. The term information comes from the Latin word informatio - explanation, exposition. The original meaning of this term is information transmitted to people.
Shannon approach to determining the amount of information
Shannon's approach to determining the amount of information. A syntactic approach to the definition of information is developed in the statistical theory of information. Shannon introduced the concept of quantity info
The concept of the system and its properties
The concept of a system and its properties. The concept of a system is widely used in science, technology, and economics when one speaks of a certain ordered totality of any content. The system is an objective unit
System classification
Classification of systems. Systems can be classified according to various criteria. In the most general terms, systems can be divided into material and abstract. Material Presentation Systems
Description of systems using information models
Description of systems using information models. An important method for studying systems is the modeling method. Its essence is that the object under study is replaced by its model, then e
Basic information processes and levels of their presentation
Basic information processes and levels of their presentation. Any information technology is composed of interconnected information processes, each of which contains a certain set of percent
Production Planning Phases
Phases of production planning. Production is organized in accordance with the plan developed in the planning phase and reflecting the model of products. In the process of functioning
Planning phase
Planning phase. At this control phase, in various time modes, several sets of functional planning tasks are solved; long-term planning for 3-5 years, annual and opera
Regulation phase
Regulation phase. At this phase, the functional tasks of scheduling and production scheduling are solved, that is, there is an operational impact on the parameters of production
Office as an information system
Office as an information system. An office is an enterprise or organization management service. The enterprise is connected by information flows with the outside world, and make optimal decisions
Electronic office
Electronic office. Solving management tasks involves working in an electronic office. An electronic office is a set of specialists and means organized to achieve a common goal.
Workflow automation
Workflow automation. In the study of information flows, great importance is attached to the proper organization of the workflow, that is, the sequence of passage of the document from the moment e
Accountant workstation
Accountant workstation. A significant role in the management process is played by accounting, where about 60 of all information is concentrated. From a modern accountant require
Local computer networks
Local computer networks. Computer Networks A computer network is a group of computers interconnected using special equipment that provides data exchange. Computer
Ethernet Topology
LAN topology. Local Area Networks are computers located within one or more adjacent buildings and connected using cables and connectors. Since electric
Global computer network internet
Global computer network Internet. WANs The expansion of local networks and lengthening of communication lines has led to the need to create distributed or global networks in which components
Network messaging methods
Methods for transmitting messages on the network. According to the method of transmitting information distinguish networks with switching channels, messages and packets. Channel switching involves the establishment of a physical connection between
Addressing users and files on the Internet
Addressing users and files on the Internet. Each user connected to the Internet has its own unique address. This address can be written in two forms as a digital IP address
Commercial Opportunities Online
Commercial Internet opportunities. Until recently, the global network was considered only as a means of storing and transmitting information. In recent years, with the advent of the WWW service on the Internet
Classification of financial and economic programs
Classification of financial and economic programs. The financial and economic application software present on the market today is very diverse and heterogeneous, which is the result
Mini-accounts
Mini-accounts. The class of mini-bookkeeping includes programs designed for bookkeeping with a small number of 1-2 people, without the explicit specialization of employees in specific sections of accounting. E
Integrated Accounting System
Integrated accounting system. Most of the developments in this class grew from the previous one. Today, the class of integrated accounting systems is one of the most common
Accounting Office
Accounting office. This is an enterprise management automation system. Such developments are built not so much for the accountant as for the manager. The accounting component here
Legal systems and databases
Legal systems and databases. This class includes systems for the operation, storage and regular updating of collections of regulatory documents. Managers and specialists of enterprises
 sotikteam.ru Smartphones. Antiviruses. Programs. Instructions. Browsers
sotikteam.ru Smartphones. Antiviruses. Programs. Instructions. Browsers